One of the hardest things for many people to conceptualize when talking about how fast something is going is that they must ask, “Compared to what?” All motion only makes sense from a frame of reference, and many spacecraft traveling in the depths of the void lack any regular reference from which to understand how fast they’re going. There have been several different techniques to try to solve this problem, but one of the ones that have been in development the longest is StarNAV – a way to navigate in space using only the stars.
Several projects named “StarNAV” seem to be ongoing at various stages of development, including a NASA Institute for Advanced Concepts grant for some researchers on the East Coast of the US and a small start-up company based on technology out of UC Irvine. In this case, we’ll look at the work done by the researchers, particularly a paper they released last year detailing some progress toward a prototype.
The technology developed by Paul McKee of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Hoang Nguyen and Michael Kudenov of North Carolina State, and John Christian of Georgia Tech is based on a specific feature of stars known as stellar aberration. As defined in the Special Theory of Relativity, stellar aberration occurs when the velocity of an observer changes the apparent distance between it and a star.
Fraser discusses some of the difficulties of navigating in space.This technique has been used before; however, it has had wide error bands when calculating a spacecraft’s instantaneous velocity. Typically, existing solutions would use a large telescope to measure a property known as an “inter-star angle” between two stars in a relatively narrow field of view precisely. If it is precise enough, some pretty complex math can produce a spacecraft’s velocity from only one inter-star angle.
Getting a measurement that is precise enough is the tricky part. To accurately detect the position of an individual star in an inter-star pair, many telescopes have to have a narrow field of view (FOV). That narrow FOV means that only one star can be tracked per telescope, which requires a second telescope and a complicated metrology system to track the relative alignment of these telescopes.
The NIAC researchers came up with a method of using slightly less precise inter-star angle measurements but multiple measurements, and once again using fancy math to calculate an accurate velocity measurement without the complicated tracking systems.
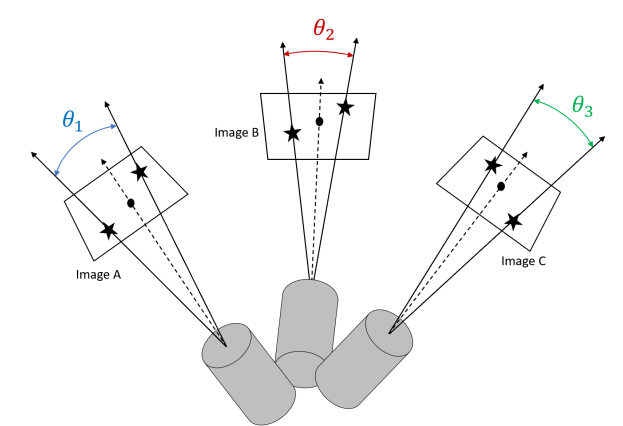 Depiction of the three telescope system described in the paper.
Depiction of the three telescope system described in the paper.
Credit – Paul McKee, Hoang Nguyen, Michael W. Kudenov, John A. Christian
The system described in the paper consists of three different telescopes offset from each other at known angles, each observing a different pair of stars. With these three slightly less precise measurements, an algorithm can still calculate an average stellar aberration and, therefore, a reasonable estimate of spacecraft velocity.
If there wasn’t enough math in this process already, the authors decided to prove the accuracy of their system by running some experiments using every mathematician’s favorite random test algorithm – a Monte Carlo simulation. While they did find some confounding factors that must be dealt with in a calibration process, the simulation proved that, in theory, at least, the system would work with an accuracy compared to the best narrow FOV solutions currently available and would be much cheaper and easier to operate.
In a final proof of concept, the researchers also modeled how big such a system would be. They fit it into a 3U cubesate chassis – measuring about 10cm x 30cm x 10cm. And because of the modularity of CubeSats designs, it might be possible to attach any such module onto another chassis as part of a fully-fledged mission.
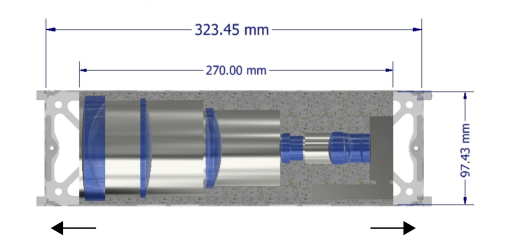 Model of StarNAV fitting into a 3U cubesat package.
Model of StarNAV fitting into a 3U cubesat package.
Credit – Paul McKee, Hoang Nguyen, Michael W. Kudenov, John A. Christian
That hasn’t happened yet, though, and it doesn’t appear that a complete prototype of this system has been built yet. Though, as mentioned above, there is a start-up looking to commercialize very similar technology, though mainly for Earth-based navigation as an alternative to GPS – they have several military contracts, who would be looking for ways to continue navigation if GPS happens to be knocked out of commission by enemy action.
As more and more spacecraft start venturing into deep space, improving how they calculate their velocity will become an ever-increasing problem. StarNAV seems well placed to do so – it just needs a bit more of a push into the prototyping stage to get there.
Learn More:
McKee et al – StarNAV with a Wide Field-of-View Optical Sensor
UT – Let the Robot Take the Wheel. Autonomous Navigation in Space
UT – Traveling the Solar System with Pulsar Navigation
UT – Navigating the Solar System Using Pulsars as GPS
Lead Image:
Optical setup similar to the ones used on StarNAV’s telescopes.
Credit – Paul McKee, Hoang Nguyen, Michael W. Kudenov, John A. Christian

