Auroral fireworks for Halloween? It just might happen, depending on where you live.
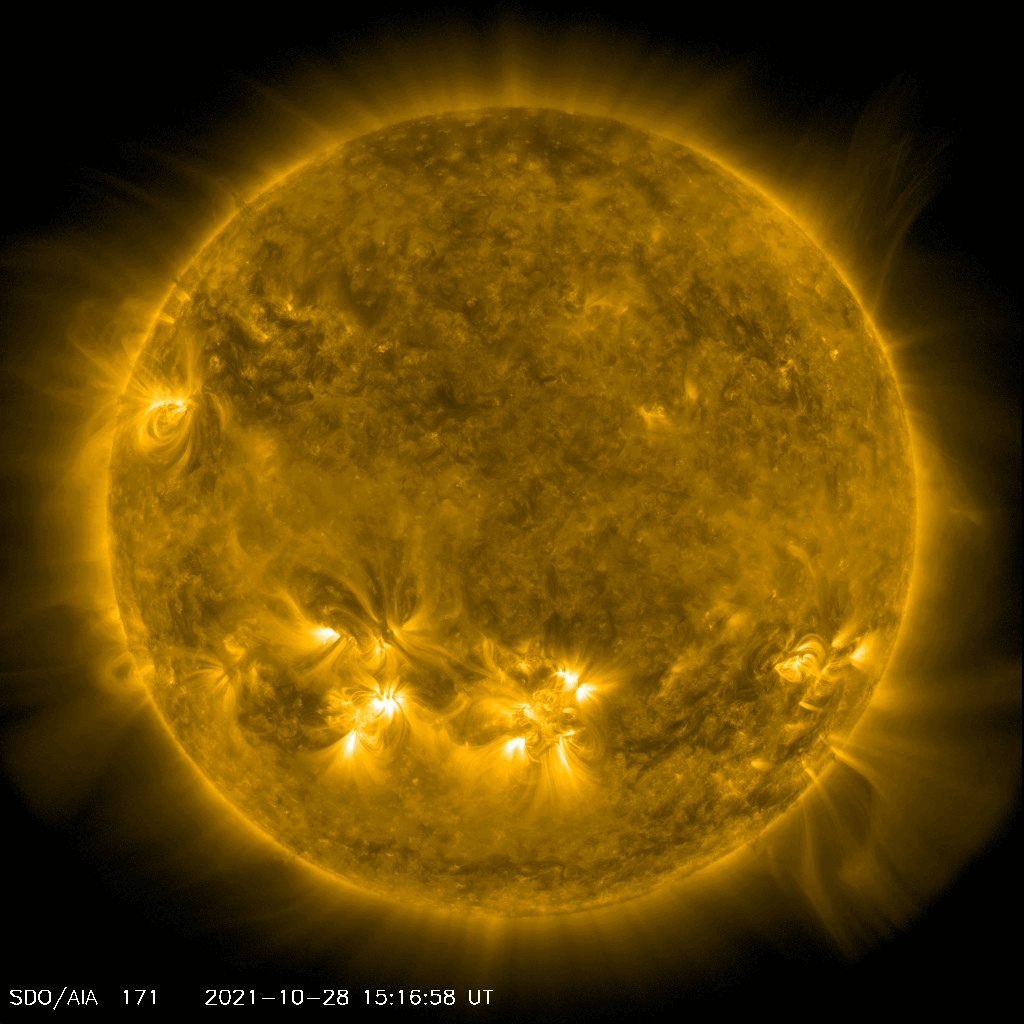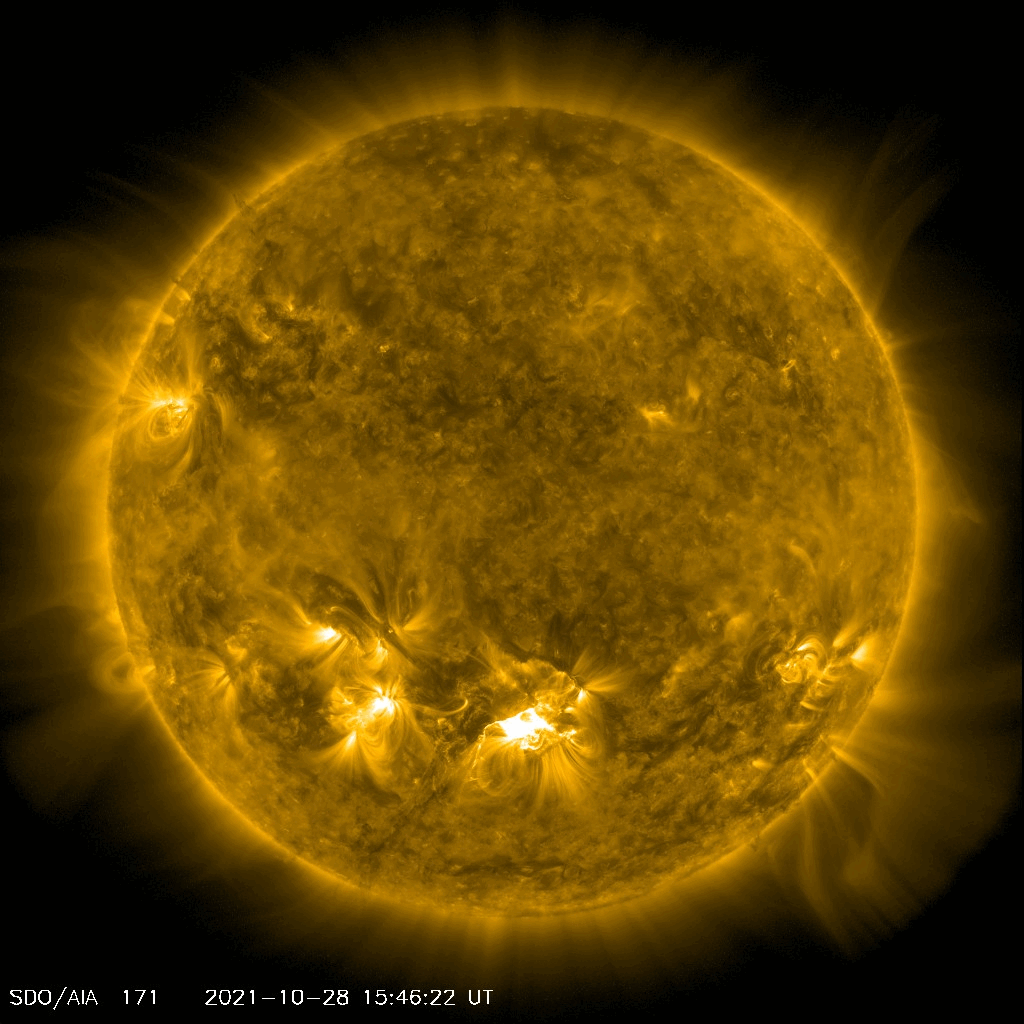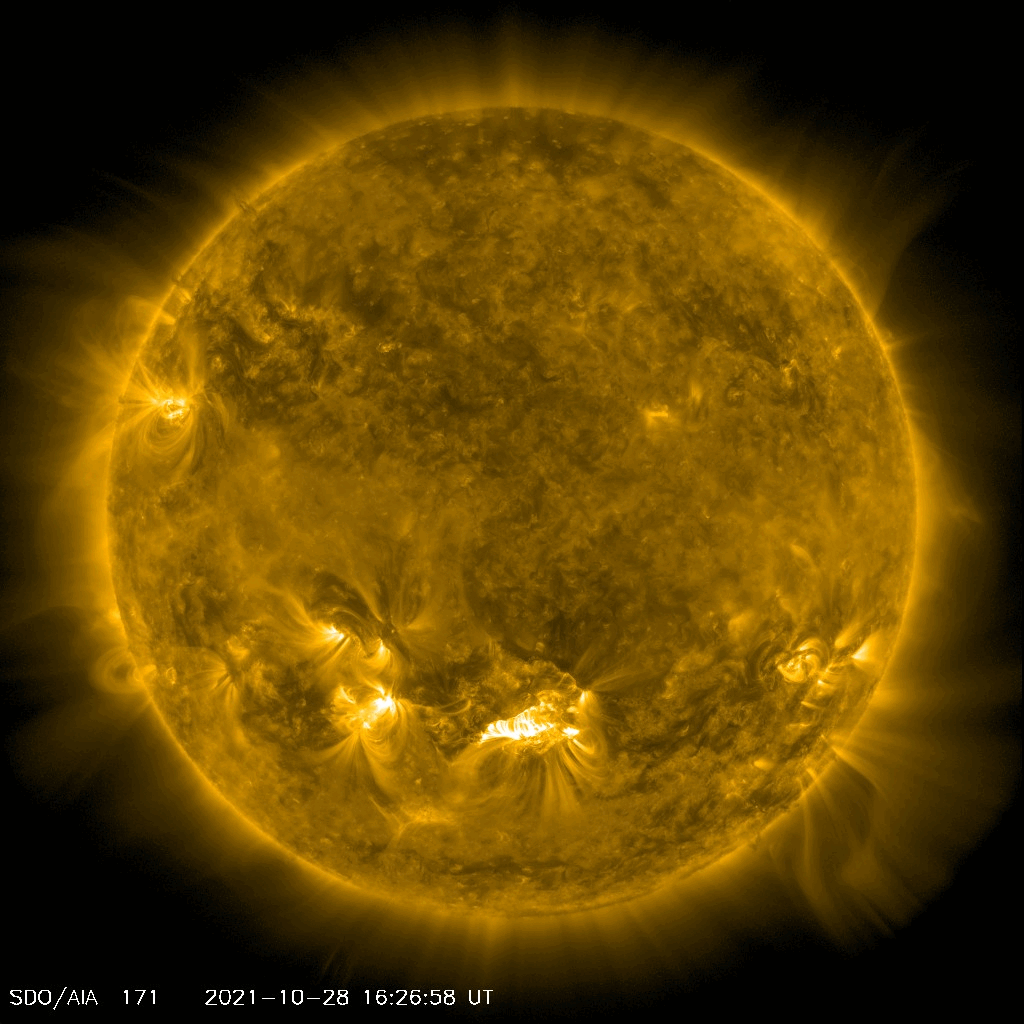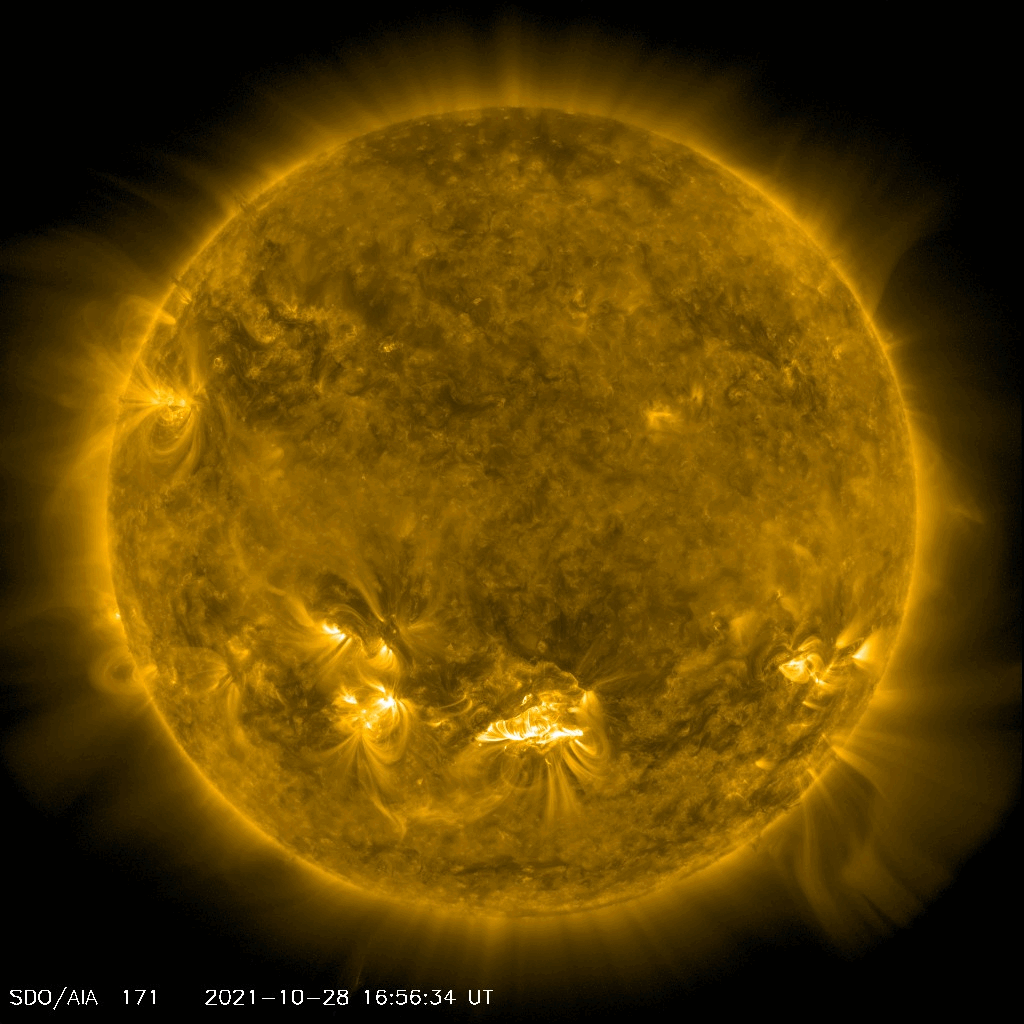 NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this movie of a solar flare — as seen in the bright flash at the Sun’s lower center — on Oct. 28, 2021. Credit: NASA/SDO
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this movie of a solar flare — as seen in the bright flash at the Sun’s lower center — on Oct. 28, 2021. Credit: NASA/SDOOn October 28, 2021 the Sun blasted a “significant” X1 solar flare – the most intense class of flares. While the flare itself hit Earth eight and a half minutes later, an accompanying Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) was also released. The slower moving CME arrives on October 30, and when it hits Earth’s magnetic field, a strong geomagnetic storm is possible on the 30th and possibly into the 31st as Earth continues to pass through the CME’s wake.
This should make for spectacular auroras in both hemispheres, aurora borealis in the north and the aurora australis in the south.
NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center issued a G3 (Strong) geomagnetic storm watch for October 30th. In the past, this type of flare has produced auroras visible to the unaided eye as far south as Illinois and Oregon in the US, typically 50° geomagnetic latitude, according to SpaceWeather.com.
 Via the Space Weather Prediction Center.
Via the Space Weather Prediction Center.X-class denotes the most intense flares (smallest flares are A-class) and the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc. Flares that are classified X10 or stronger are considered unusually intense, but X1 is still considered a major flare.
The Sun has been active lately (see aurora imagery from the CME that reached Earth in mid-October) as you can see from this movie from SDO data, processed by Seán Doran.
Have questions about the various classes of solar flares and what they mean for Earth? Here’s an excellent guide to solar flares from NASA:
Lead image caption: NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of a solar flare — as seen in the bright flash at the Sun’s lower center — on Oct. 28, 2021. The image shows a subset of extreme ultraviolet light that highlights the extremely hot material in flares and which is colorized here in teal. Credit: NASA/SDO

